LASER THERAPY: The Most Effective Alternative Treatment for Chronic Knee Pain
What is chronic knee pain?
Chronic knee pain is long-term pain, swelling, or sensitivity in one or both knees. The cause of your knee pain can determine the symptoms you experience (severe pain on the knee, burning and pricking pain at medial aspect, difficulty in walking and folding knee, climbing and sitting on the floor).
What causes chronic knee pain?
Temporary knee pain is different from chronic knee pain. Many people experience temporary knee pain as a result of an injury, sudden infection or accident. Chronic knee pain rarely goes away long period. Diseases and causes or conditions that give severe knee pain are:
- Osteoarthritis: pain, inflammation, and joint destruction caused by degeneration and deterioration of the joint (Age-related degeneration and excess weight)
- Tendinitis: pain in the front of the knee that is made worse when climbing, taking stairs, or walking up an incline
- Bursitis: inflammation caused by repeated overuse or injury of the knee
- Chondromalacia patella: damaged cartilage under the kneecap
- Gout: arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid
- Baker’s cyst: a buildup of synovial fluid (fluid that lubricates the joint) behind the knee
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder that causes painful swelling and can eventually cause joint deformity and bone erosion
- Dislocation: dislocation of the kneecap most often the result of trauma
- Meniscus tear: a rupture in one or more of the cartilage in the knee
- Torn ligament: tear in one of the four ligaments in the knee — the most commonly injured ligament is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Who is at risk for chronic knee pain?
People who are overweight or obese are at a greater risk for knee problems. Other factors that increase your risk for chronic knee pain include ( age, previous injuries or trauma, athletic activity or physical exercise, Calcium deficiency, Insufficient Vit D3)
Diagnosis
Each possible cause of chronic knee pain requires different diagnostic tests. These include blood work, physical examination, X-rays, CT scan or MRI, and other imaging tests.
Treating chronic knee pain
Each underlying cause of chronic knee pain has a specific type of treatment.
- Low-Intensity Laser Therapy
- USG Therapy
- physical therapy and exercise, walk
- Massage therapy (oil or ointment massage)
- Acupuncture therapy
- Medication (NSAIDs, Glucosamine, Calcium, Vit D3, Anti rheumatoid)
- Surgery (Arthroscopy, Total knee replacement)
- Injections
- Weight loss
Prevention
Laser Therapy every 3 months reactivate dose can prevent more destruction and inflammation.
Lasers for DEEP Tissue and Bone Therapy:
Laser Therapy is used for the relief of pain, to accelerate healing and decrease inflammation. When the light source is placed against the skin, the photons penetrate several centimeters and get absorbed by the mitochondria, the energy-producing part of a cell. This energy fuels many positive physiological responses resulting in the restoration of normal cell morphology and function. Laser Therapy has been successfully used to treat a broad range of medical conditions, including musculoskeletal problems, arthritis, Nerve compression, PIVD, Buerger’s disease, DVT, Lymphangitis, sports injuries, soft tissue injury, non-healing wounds, ENT diseases, piles, fissure, Stroke with paralysis, diabetic ulcers and dermatological conditions.
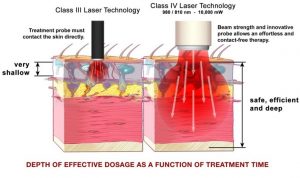
The central goal of laser therapy is to stimulate the cell to perform its natural functions but at an enhanced rate. Targeted in hemoglobin and cytochrome oxidase, the high power diode laser could help the respiration and then in result have a good performance therapy. In sharp contrast to “Cold lasers” which provide no feeling or sensation, high power diode laser therapy will provide warm and soothing feeling.
Medicines only address the symptoms of the disease for short term until taking. Laser Therapy treats the underlying condition or pathology to promote healing. This means that the treatments are effective and the benefits of Laser Therapy are long-lasting.
What are the Benefits of Laser Therapy?
Treatment is painless, Highly effective for many diseases and conditions, Eliminates pain. Reduces the need for medicines, Restores normal range of motion and physical function, Easily applied, Non-invasive, Non-toxic, No known adverse effects, No drug interactions, Often makes surgical interventions unnecessary, Provides a treatment alternative for patients that have not responded to other therapies.
Biological Effects:
· Anti-Inflammation
Laser therapy has an anti-edema effect as it causes vasodilatation, but also because it activates the lymphatic drainage system (drains swollen areas). As a result, there is a reduction in swelling caused by bruising or inflammation.
· Anti-Pain (Analgesic
Laser therapy has a highly beneficial effect on nerve cells which block pain transmitted by these cells to the brain and which decreases nerve sensitivity. Also, due to less inflammation, there is less edema and less pain.
· Accelerated Tissue Repair and Cell Growth
Photons of light from lasers penetrate deeply into tissue and accelerate cellular reproduction and growth. The laser light increases the energy available to the cell so that the cell can take on nutrients faster and get rid of waste products.
· Improved Vascular Activity
Laser light will significantly increase the formation of new capillaries in damaged tissue that speeds up the healing process, closes wounds quickly and reduces scar tissue.
Increased Metabolic Activity
· Laser therapy creates higher outputs of specific enzymes, greater oxygen and food particle loads for blood cells.
· Trigger Points and Acupuncture Points is also effective
CONCLUSION:
The present study demonstrated that 830 nm LLLT was an effective form of treatment for chronic knee pain caused by knee osteoarthritis. No need to sit home if anybody says your knee is untreatable; Laser Therapy can give new hope of pain-free knee and easy walk.
